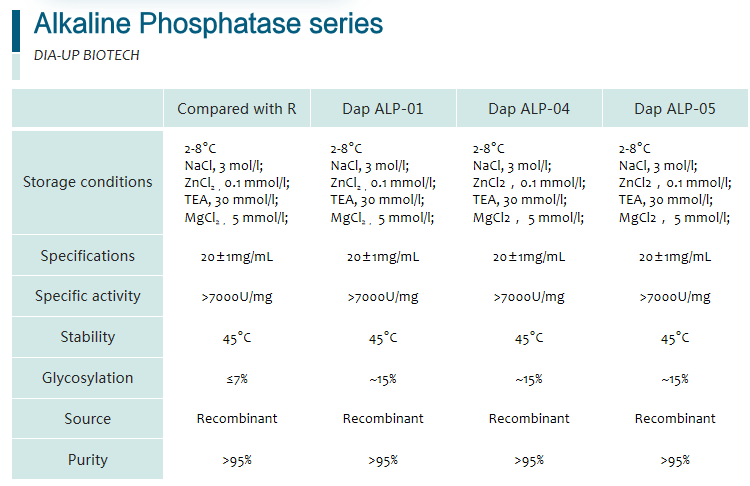


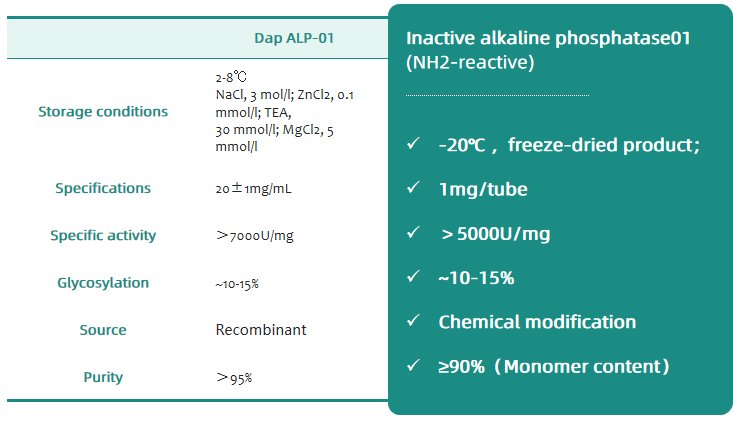
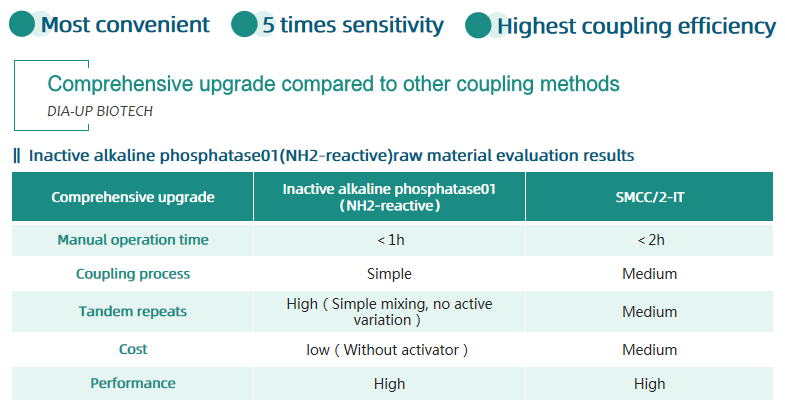
BEIJING DIA-UP BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO.,LTD
Sales hotline:+86185 1363 7053
Service hotline:+86185 1363 7192
After-sales hotline:+86185 1363 7531
Order Email:order@dia-up.com
After-sales Email:service@dia-up.com
Official website:www.dia-up.com
Company Add:Building 18, No. 2, Huankexizhong Road, Tongzhou District, Beijing